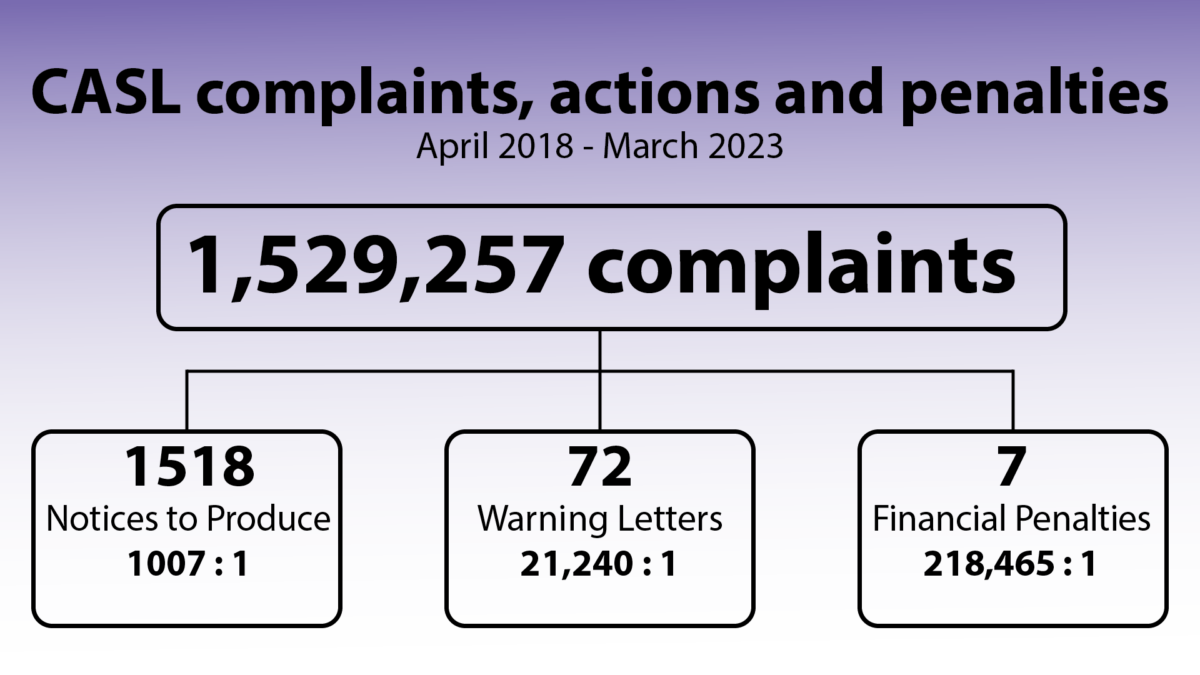
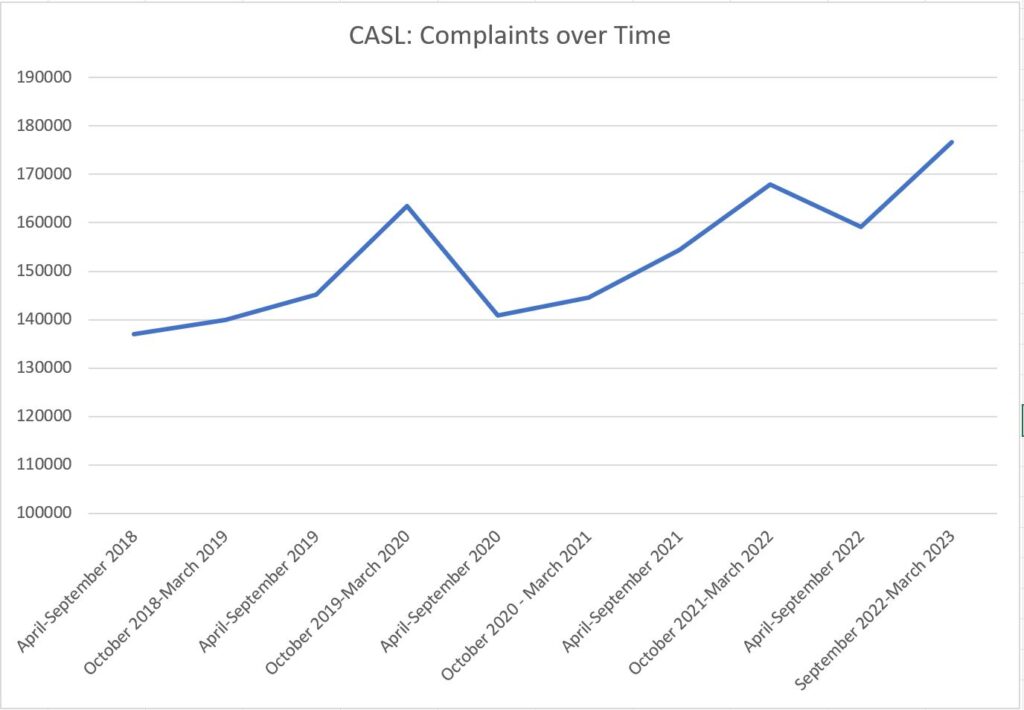
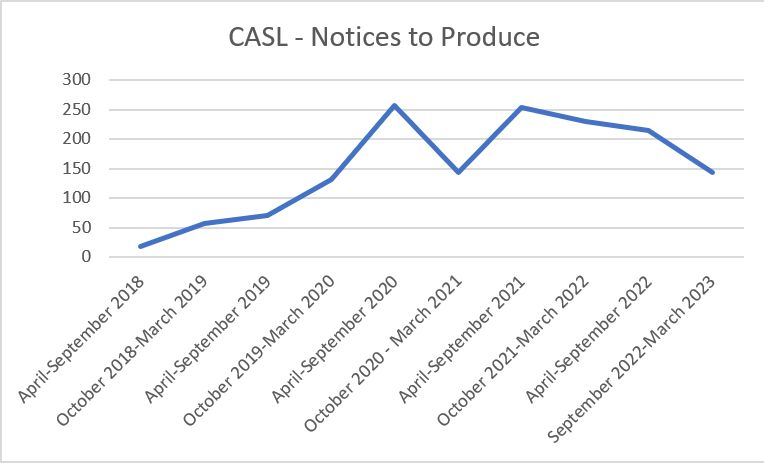
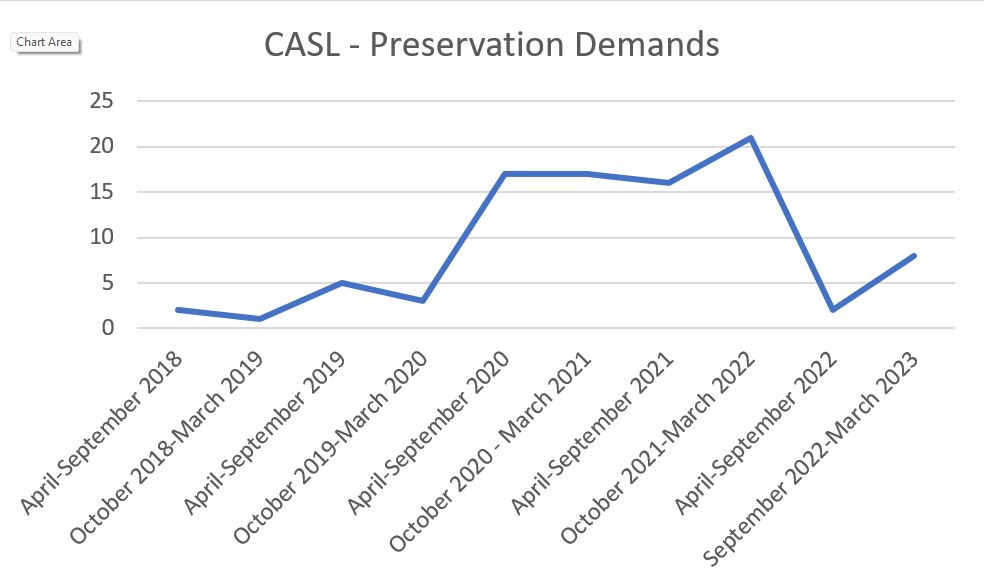
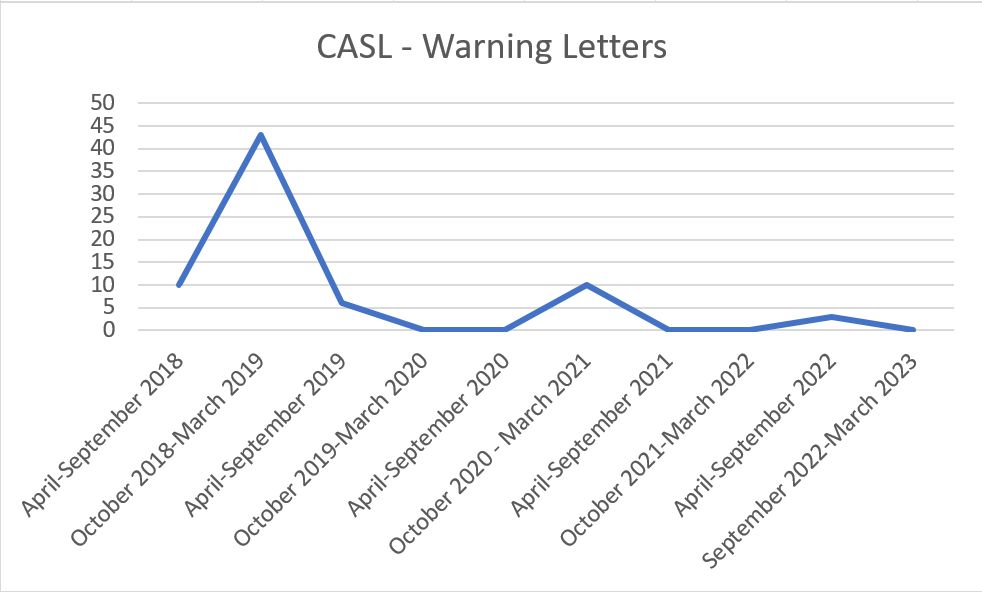
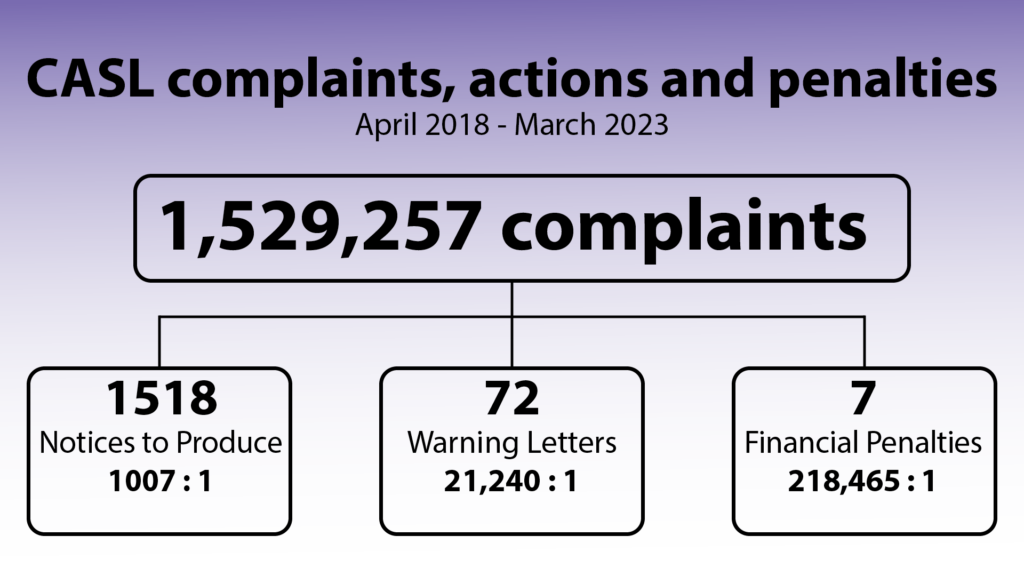
This is part six of a multi-part series reviewing Canada’s Anti-Spam Legislation in practice since its introduction in 2014 and the beginnings of enforcement in 2015. Crosslinks will be added as new parts go up.
Part 1: Terminology
Part 4: Case File – Compu-Finder
Part 5: Case File Anthology, 2015-2016
Part 6: Case File – Blackstone Education
Part 7: Case File Anthology, 2017-2018
Part 8: Case File – Brian Conley/nCrowd
Part 9: Case File Anthology, 2019-2022
Core resources:
Enforcement Actions Table (CASL selected)
I had set Blackstone aside because it looked like an education space company, but now that I’m in it, it’s a training company, and on its face looks very similar to Compu-Finder.
This on its own is not necessarily proof of anything – correlation is not causation – but companies that push for-profit training courses seem to come up a lot in CASL decisions. Unlike Compu-Finder, Blackstone Seminars/Blackstone Learning Solutions/Blackstone Professional Development Group seems to be soldiering on. Their online presence doesn’t suggest great health, though: the site looks like it’s been coded to viewports that are only about 800px wide, which suggests it hasn’t been touched since 800×600 was king of the display resolutions, which was, uh, 2005?
I know this is a bit obsessive but I care about UX and accessibility, and for a company that is supposed to be providing training to the government, from whence all accessibility legislation hath come, this seems just ridiculous to me:
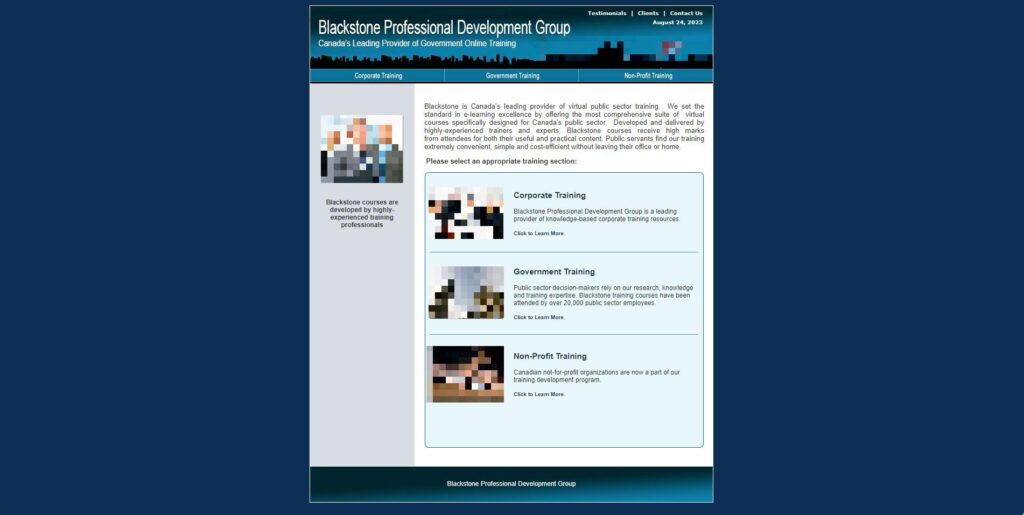
Anyway – back in 2014, when pretty much all computer monitors accommodated much wider resolutions than 800px1sorry, I’ll stop now, Blackstone was served a Notice to Produce (NTP). An initial deadline of November 21 was extended to December 3 at Blackstone’s request, and then – well, let me just flip the entire thing into an accordion here, emphasis in the original:
Compliance and Enforcement Commission Letter Addressed to Ari Rozin (Blackstone Learning Corp.)
Ottawa, 22 January 2015
BY E-MAIL AND COURIER
Our File No.: 9102-201400305-010
(…)
Ari Rozin
Blackstone Learning Corp.
107 Weslock Cres., Unit 2B
Aurora, Ontario L4G 7Z4
Re: Notice to Produce in File No. 9102-201400305-010 – Request for review from Blackstone Learning Corp.
On 7 November 2014, pursuant to An Act to promote the efficiency and adaptability of the Canadian economy by regulating certain activities that discourage reliance on electronic means of carrying out commercial activities, and to amend the Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission Act, the Competition Act, the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act and the Telecommunications Act (the Act), a designated person for the purpose of section 17 of the Act served a notice to produce (NTP) on Blackstone Learning Corp. (Blackstone)
The NTP required Blackstone to produce certain documents by 21 November 2014. On 20 November 2014, this deadline was extended to 3 December 2014 by the designated person, at Blackstone’s request. Blackstone subsequently sought a review of the NTP.
Section 18(1) of the Act provides that an application by a person for review of an NTP must be brought before they are required to produce a document.
Part 5 of the NTP served on Blackstone also provides that a request for review must occur within the time limit set out in Part 3 of the Notice, and establishes the process for making such an application to the Commission by fax or postal mail. Blackstone was also informed by emails from the designated person dated 26 and 27 November 2014 that it needed to follow the procedure set out in Part 5, and needed to comply with the extended deadline.
On 4 December 2014, Blackstone sent an email to the designated person stating, “Please consider this a formal request for a review based on the unreasonable request to produce the documents in the given time.”
The Commission notes that Blackstone was made aware of the applicable procedure and deadline for requesting a review both by the NTP itself, and through emails exchanged with the designated person. The Commission considers that Blackstone’s request for review, which was made by email after the 3 December 2014 deadline, provides no explanation as to why it was unable to comply with the deadline, and gives no reasons why a late submission should be accepted by the Commission. The Commission notes that even if Blackstone’s request had been made within the applicable deadline, it provides no reasons or arguments to support its assertion that the NTP is unreasonable.
In light of these considerations, the Commission denies Blackstone’s request for review on the basis that it does not conform to the procedures established in the NTP, or with the requirement in section 18(1) of the Act that such an application be brought before the documents at issue are required. Blackstone is therefore required to produce the documents specified in the NTP in the form and manner set out therein, to the designated person, by 29 January 2015.
Pursuant to subsection 18(5) and section 27 of the Act, Blackstone has the right to appeal this decision by bringing an appeal in the Federal Court of Appeal within 30 days after the day on which the decision is made. An appeal on a question of fact may be brought only with the leave of the Federal Court of Appeal, an application for which must be made within 30 days after the day on which the decision is made. An appeal with leave may not be brought later than 30 days after the day on which leave to appeal is granted.
Sincerely,
John Traversy
Secretary General
If you haven’t looked at it, flip that thing open and take a look at that last paragraph, which explicitly lays out how to appeal this decision with the Federal Court of Appeal.
Blackstone instead apparently filed an application for leave to appeal with the Supreme Court of Canada, which is not the Federal Court of Appeal.2I can’t find the Application for Leave to Appeal on the SCC website, but that might be because it didn’t even get heard – per this CRTC decision, s8-12, the SCC Registrar wrote back and copied the Commission that the SCC was not the right venue. This doesn’t seem to exist in any findable online archive.
The Supreme Court replied to Blackstone – wrong venue! – and then Blackstone did not appeal with the Federal Court, for some reason.
But – while I am not a lawyer (and this is not legal advice) – I’d think that somebody at Blackstone would have very sharp words for their counsel for not understanding the fundamentals of how appeals work, and not even reading the NTP request letter or follow-up directive of January 22.
So – after an odd digression into inappropriate leaves for appeal – the CRTC issued its decision on October 16, 2016.
Worthy of note:
- A campaign is a violation, not an individual email: [2]”The notice identified nine messaging campaigns totalling 385,668 commercial electronic messages sent by Blackstone between 9 July and 18 September 2014 without the consent of the recipients. As a result, a designated person stated that they had reasonable grounds to believe that Blackstone had committed nine violations of paragraph 6(1)(a) of the Act.”
- You don’t need a price to appear to be selling something: [18] “The cost of these programs was not specifically discussed; however, the nature of the language used, including references to various discounts and group rates, conveyed that these courses were services available for purchase from Blackstone. The Commission thus determines that the messages were sent for the purpose of advertising and promoting services commercially available from Blackstone, and were commercial electronic messages within the meaning of subsection 1(2) of the Act.”
- A bit of unpacking around how publishing an email address on the Internet is supposed to work re. “conspicuous publication” in para. 10(9)(b) of the Act [25-28 of the CRTC decision] – key phrase being “the Act does not provide persons sending commercial electronic messages with a broad licence to contact any electronic address they find online; rather, it provides for circumstances in which consent can be implied by such publication, to be evaluated on a case-by-case basis. Pursuant to section 13 of the Act, the onus of proving consent, including the elements of implied consent under paragraph 10(9)(b) of the Act, rests with the person relying on it.”
- Other than complaining initially about timelines and the AMP amount, and the misguided appeal to the Supreme Court, Blackstone doesn’t appear to have cooperated with the CRTC at all; [55] “Blackstone did not cooperate with the investigation. The company refused to respond to a notice to produce issued under section 17 of the Act, even after a Commission decision requiring that it do so.”
And – despite Blackstone essentially just filing complaints and misfiling appeals and not doing anything that the Commission asks them to do – the CRTC still lowers the AMP from $640,000 to $50,000.
Once again, like with Compu-Finder, there’s what feels like almost a tacit admission that they do this to terrify marketers into compliance: [60] “As stated in the Act, the purpose of a penalty is to promote compliance with the Act, and not to punish. To this end, the penalty set out in the notice of violation places great emphasis on the principle of general deterrence. The Commission accepts that this is a valid principle to be considered in the imposition of an AMP, but considers that the specific circumstances of Blackstone’s case, and the violations that have taken place, require a lower AMP.”
Why the drop to $50,000? Because [61-62] Blackstone is a small business; its belief that it had consent was established before the release of the 2015-published Guidance on Implied Consent; along with the idea that other regimes like the Unsolicited Telecommunications Rules have lower penalties and still result in compliance.
Which — look, I am supportive of the CRTC and CASL. I understand the logic of the stunning amounts announced in terms of their value as deterrents. But there’s a bit of “boy who cried wolf” here — a risk of normalizing the process of not taking large judgments that seriously because you can be certain they’ll be amended downward.3As an aside, an early post-lockdown internal comms issue was mask enforcement. It was mandated and we were announcing that masks must be worn in buildings, with certain exceptions for eating/drinking. But practically, who would enforce those rules during campus open hours, continuously, in all areas? As I was saying at that time, if you can’t meaningfully monitor and enforce rules globally, the second approach is to make punishment so draconian that it is terrifying to anyone that contemplates breaking the rule. But the #1 rule of terrifying punishments is that you kind of have to stick to the terrifying component. “We will announce the iron maiden but walk it back to a brisk tickling” over time is in some respects worse than just appealing to the common good.
This was also in yesterday’s 2015-16 round-up, but just so the tally is close at hand:
Issued penalty: $640,000
Final penalty: $50,000
Total issued AMPs: $2,192,000
Total imposed AMPs/monetary penalties: $908,000
Differential: $1,284,000
- 1sorry, I’ll stop now
- 2I can’t find the Application for Leave to Appeal on the SCC website, but that might be because it didn’t even get heard – per this CRTC decision, s8-12, the SCC Registrar wrote back and copied the Commission that the SCC was not the right venue. This doesn’t seem to exist in any findable online archive.
- 3As an aside, an early post-lockdown internal comms issue was mask enforcement. It was mandated and we were announcing that masks must be worn in buildings, with certain exceptions for eating/drinking. But practically, who would enforce those rules during campus open hours, continuously, in all areas? As I was saying at that time, if you can’t meaningfully monitor and enforce rules globally, the second approach is to make punishment so draconian that it is terrifying to anyone that contemplates breaking the rule. But the #1 rule of terrifying punishments is that you kind of have to stick to the terrifying component. “We will announce the iron maiden but walk it back to a brisk tickling” over time is in some respects worse than just appealing to the common good.